| Quick Facts: | Lake Agassiz |
|---|---|
| Countries: | Canada & USA |
| Area: | 285.000 km² (110.000 mi²) |
| Main Rivers: | Abitibi River |
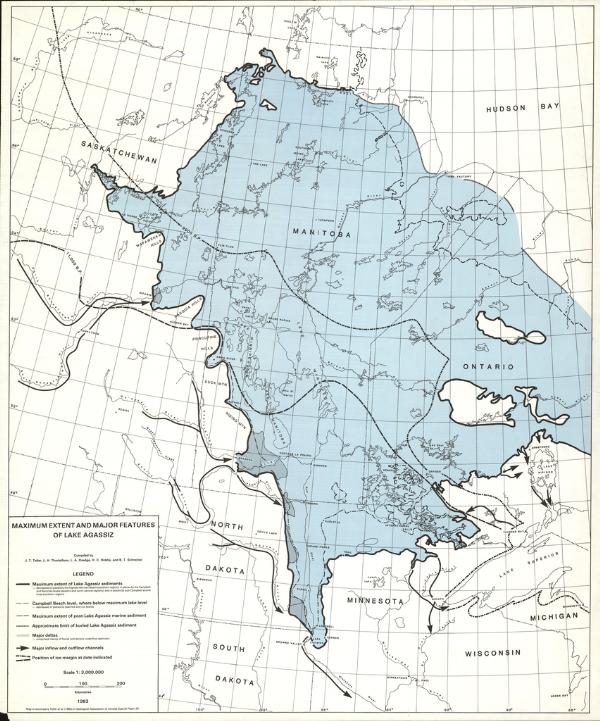
The Lake Agassiz is the name of a large shallow glacial lake that existed in North America during the Pleistocene Period. About 110,000 square miles (285,000 sq km) in area, it covered most of what is now southern Manitoba and parts of Saskatchewan, Ontario, North Dakota, and Minnesota.
As the continental ice sheet retreated, its melting waters formed Lake Agassiz, which found its outlet to the south because the normal northward drainage of the region was blocked by ice.
When the ice melted completely, the lake drained away to the north. Lakes Winnipeg, Manitoba, and Winnipegosis and Lake of the Woods are remnants of Lake Agassiz, a large part of whose bed is now the fertile wheatland valley of the Red River of the North.
The lake was named in 1879 for the Swiss American naturalist Louis Agassiz, who had demonstrated that much of North America was covered by a vast glacier during the geologic epoch preceding the present one.